Use Sanger Sequencing and Fragment Analysis to learn about your maternal or paternal roots.
Use the family finder feature in FamilyVault to potentially view and connect with matched relatives.
Trace your migration pattern of your ancient ancestors from thousands of years ago to today.
Trace your paternal ancestry.
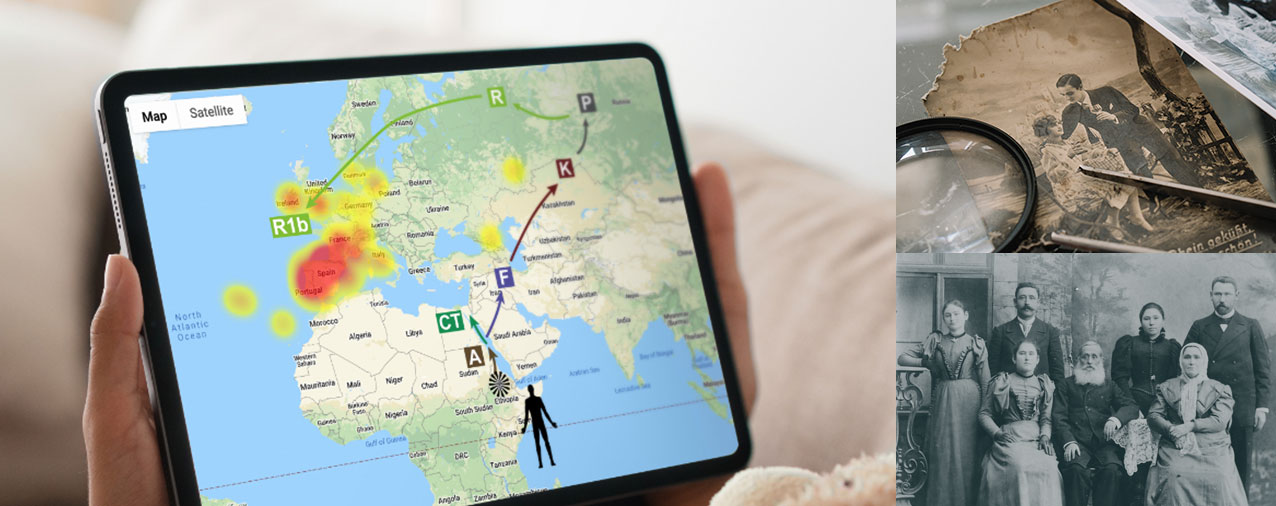
Your Y-DNA is your link back to all of your paternal ancestors. It is passed down unchanged from father to son and is the only way to accurately trace your paternal ancestry.
Your Y-DNA contains both slow and fast-changing genetic markers. DNA SNP chips (used by many of our competitors) detect slow-changing SNPs, which are excellent for tracing ancient ancestry but useless for anything recent (i.e. the last few hundred years). So if you want to use your DNA to help build your family tree, you need to look at fast-changing genetic markers – STRs. And that is exactly what our test detects – STRs found on your Y chromosome.
Our paternal ancestry test can analyze 20, 44 or 101 different Y-DNA STRs. The choice is yours, and the more you choose, the higher your resolution will be. Compare your Y-DNA to published data from hundreds of famous historical figures and ethnic groups around the world. Our test even allows two males to determine how many generations ago they shared a common ancestor.
Important! This test can only be taken by MALES, as only males have Y-DNA. Females wishing to trace their own paternal lineage must test the Y-DNA of a direct male line relative.
Features:
- Trace your recent ancestry
- Define your paternal ethnic background
- Understand your paternal origins
- Search a global database for long-lost relatives on your paternal line
- Compare your Y-DNA against famous people throughout history, including famous and infamous individuals, royalty, outlaws, world leaders, poets, and more
- Painless buccal (mouth) swab sample collection
- All tests are run 2x for absolute accuracy
- Quickly collect samples in the privacy of your own home
- 24/7 online test status check
- No age limit
- State-of-the-art accredited testing laboratory
What is Y-DNA?
Y-DNA refers to the DNA on the male sex chromosome – the Y chromosome. We each have 23 pairs of chromosomes: 22 pairs of autosomal chromosomes and two sex chromosomes – the X and Y chromosomes. Females inherit an X chromosomes from each parent (but no Y chromosome), while males inherit an X chromosome from their mother and a Y chromosome from their father. Very little recombination (mixing) occurs between the X and Y chromosomes in males, hence the Y-DNA essentially remains unchanged through the paternal line, providing an incredibly useful way to trace paternal ancestry.
What is the Y-DNA STR test?
The Y-DNA STR test is a useful technique used in ancestry, relationship and forensic applications. The test analyzes markers in the Y chromosome known as STRs or ‘short tandem repeats’. STR markers are short segments of DNA (2-13 nucleotides in length), which are repeated multiple times. STR analyses measure the exact number of repeat units. The number of repeats differs between individuals because STRs change frequently. The more closely related two individuals are along their direct paternal line, the more similar their Y-DNA STR profiles will be. Y-DNA STR tests can be used for forensic applications, investigating relationships, tracing distant male relatives who may have descended from the same paternal lineage and identifying links to famous people. It is a simple test that can provide you with rich information about your paternal lineage.
Methods and analysis of Y-DNA STR testing:
The Y-DNA STR Marker test uses a technique called polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to examine a defined set of STR markers in your Y-DNA. This technique determines the number of repeats at each marker tested – either 20, 44 or 101 markers, depending on the requested analysis. When two individuals take the Y-DNA STR marker test, their STR numbers can be compared to see if there is a match. The confidence with which the Y-DNA STR test can predict a relationship between two individuals increases as more STR markers are tested. A calculation called “TMRCA” (time to most recent common ancestor) can be performed to estimate how many generations ago the two males likely shared a common paternal ancestor. Comparing more Y-DNA STR markers will provide a higher stringency comparison and a more precise TMRCA calculation.
Trace your paternal ancestry.

Your Y-DNA is your link back to all of your paternal ancestors. It is passed down unchanged from father to son and is the only way to accurately trace your paternal ancestry.
Your Y-DNA contains both slow and fast-changing genetic markers. DNA SNP chips (used by many of our competitors) detect slow-changing SNPs, which are excellent for tracing ancient ancestry but useless for anything recent (i.e. the last few hundred years). So if you want to use your DNA to help build your family tree, you need to look at fast-changing genetic markers – STRs. And that is exactly what our test detects – STRs found on your Y chromosome.
Our paternal ancestry test can analyze 20, 44 or 101 different Y-DNA STRs. The choice is yours, and the more you choose, the higher your resolution will be. Compare your Y-DNA to published data from hundreds of famous historical figures and ethnic groups around the world. Our test even allows two males to determine how many generations ago they shared a common ancestor.
Important! This test can only be taken by MALES, as only males have Y-DNA. Females wishing to trace their own paternal lineage must test the Y-DNA of a direct male line relative.
Features:
- Trace your recent ancestry
- Define your paternal ethnic background
- Understand your paternal origins
- Search a global database for long-lost relatives on your paternal line
- Compare your Y-DNA against famous people throughout history, including famous and infamous individuals, royalty, outlaws, world leaders, poets, and more
- Painless buccal (mouth) swab sample collection
- All tests are run 2x for absolute accuracy
- Quickly collect samples in the privacy of your own home
- 24/7 online test status check
- No age limit
- State-of-the-art accredited testing laboratory
What is Y-DNA?
Y-DNA refers to the DNA on the male sex chromosome – the Y chromosome. We each have 23 pairs of chromosomes: 22 pairs of autosomal chromosomes and two sex chromosomes – the X and Y chromosomes. Females inherit an X chromosomes from each parent (but no Y chromosome), while males inherit an X chromosome from their mother and a Y chromosome from their father. Very little recombination (mixing) occurs between the X and Y chromosomes in males, hence the Y-DNA essentially remains unchanged through the paternal line, providing an incredibly useful way to trace paternal ancestry.
What is the Y-DNA STR test?
The Y-DNA STR test is a useful technique used in ancestry, relationship and forensic applications. The test analyzes markers in the Y chromosome known as STRs or ‘short tandem repeats’. STR markers are short segments of DNA (2-13 nucleotides in length), which are repeated multiple times. STR analyses measure the exact number of repeat units. The number of repeats differs between individuals because STRs change frequently. The more closely related two individuals are along their direct paternal line, the more similar their Y-DNA STR profiles will be. Y-DNA STR tests can be used for forensic applications, investigating relationships, tracing distant male relatives who may have descended from the same paternal lineage and identifying links to famous people. It is a simple test that can provide you with rich information about your paternal lineage.
Methods and analysis of Y-DNA STR testing:
The Y-DNA STR Marker test uses a technique called polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to examine a defined set of STR markers in your Y-DNA. This technique determines the number of repeats at each marker tested – either 20, 44 or 101 markers, depending on the requested analysis. When two individuals take the Y-DNA STR marker test, their STR numbers can be compared to see if there is a match. The confidence with which the Y-DNA STR test can predict a relationship between two individuals increases as more STR markers are tested. A calculation called “TMRCA” (time to most recent common ancestor) can be performed to estimate how many generations ago the two males likely shared a common paternal ancestor. Comparing more Y-DNA STR markers will provide a higher stringency comparison and a more precise TMRCA calculation.
Simple sample collection
Each kit contains painless, easy-to-use mouth swabs that are used to collect your DNA.
Quality Assured
All testing is performed in our ISO 17025, AABB and CLIA certified laboratory.

Easily get results
Get 24/7 access to your results from your secure online account within days after testing begins.

Private & confidential
Your data belongs to you. We do not share your data with any third party without your permission.
How it works

Choose one or more Ancestry Test: Maternal Ancestry (males and females) or Paternal Ancestry (males only)

Your test kit includes everything you need to collect painless mouth swab samples in the privacy of your own home.

When you’re finished collecting your DNA samples, simply mail them to the lab using the prepaid shipping envelope.

Receive confidential results in your secure online portal with free lifetime access to FamilyVault.
FAQ
Here are the answers to the most frequently asked questions about this test.
DNA is collected by rubbing a brush gently inside the mouth against the cheek for 30 seconds. The collection is safe and painless.
Please note: Ancestry testing can be done using forensic samples. To learn more about forensic sample types, please click here.
Y-DNA refers to the DNA on the male sex chromosome – the Y chromosome. We each have 23 pairs of chromosomes: 22 pairs of autosomal chromosomes and two sex chromosomes – the X and Y chromosomes. Females inherit two X chromosomes (one from each parent), while males inherit an X chromosome from their mother and a Y chromosome from their father.
Y-DNA is the only DNA which is passed down strictly from father to son along the direct paternal line (from father to son to grandson etc.). The strict patrilineal inheritance pattern of Y-DNA means that your Y-DNA profile is unique to your paternal lineage and shared by all people who descended from the same patrilineal ancestral lineage as you. Testing your Y-DNA allows you to trace your direct paternal ancestry (your father’s, father’s, father’s… paternal line).
STR markers are “short tandem repeats” – segments of DNA (2-13 nucleotides in length) which are repeated multiple times. Y-DNA STRs are the STRs that are found only on the Y-chromosome (male chromosome).
STR analysis measures the exact number of repeat units. The number of repeats differs between individuals because STRs change frequently. The more closely related two individuals are along their direct paternal line, the more similar their Y-DNA STR profiles will be.
Our Y-DNA STR tests use a technique called polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to examine a defined set of STR markers in your Y-DNA. This technique determines the number of repeats at each marker tested – either 20, 44 or 101 markers, depending on the requested analysis. When two individuals take the Y-DNA STR marker test, their STR numbers can be compared to see if there is a match. The confidence with which the Y-DNA STR test can predict a relationship between two individuals increases as more STR markers are tested. A calculation called “TMRCA” (time to most recent common ancestor) can be performed to estimate how many generations ago the two males likely shared a common paternal ancestor. Comparing more Y-DNA STR markers will provide a higher stringency comparison and a more precise TMRCA calculation.
Y-DNA STR tests can be used for forensic applications, investigating relationships, tracing distant male relatives who may have descended from the same paternal lineage and identifying links to famous people. It is a simple test that can provide you with rich information about your paternal lineage.
No. Y-DNA tests are only available to males, as only males have Y-DNA. Females wishing to trace their paternal lineage must test the Y-DNA of a male relative along their direct paternal line, such as a brother, father, male cousin, uncle, etc.
Using mtDNA sequencing and/or Y-DNA results, any two individuals can compare their profiles to see whether they descended from the same maternal line (for mtDNA) or paternal line (for Y-DNA). If the tests show that two individuals have different mtDNA and Y-DNA profiles, it would conclusively prove that they did not descend from the same maternal and paternal lineages. You can use your mtDNA and Y-DNA profiles to compare with other individuals in your tree to confirm a positive linkage, verify new linkages, or verify findings from your paper research. You can also use your mtDNA and Y-DNA markers to search our global database to find potential matches from around the world. Free lifetime access to the database is included.
Yes, your results are 100% confidential. No one will be able to access your account or your results unless you give them your confidential account login. You can change the password to your account at any time. Please remember to safeguard your login information and not share it with anyone.
When you activate your DNA Ancestry test kit online, you will have access to your secure online portal. You can check test status and download your DNA Ancestry test results as soon as they are ready. You may also navigate through the Ancestry Database directly from this portal.







